APIs are currently utilized for interaction not just between external systems or, for example, developing extensions/add-ons for any service/CMS, but also between big logical blocks within a single software environment. What exactly is the point of it? In specialist industries, this is necessary for quick performance scaling.
Each sample of a self-contained module may be executed within virtual containers using an API-based (API First) architecture (Kubernetes, Docker etc.). For subsequent maintenance, a container should be outsourced to the most appropriate server platform.
Table of Contents
What is an API?
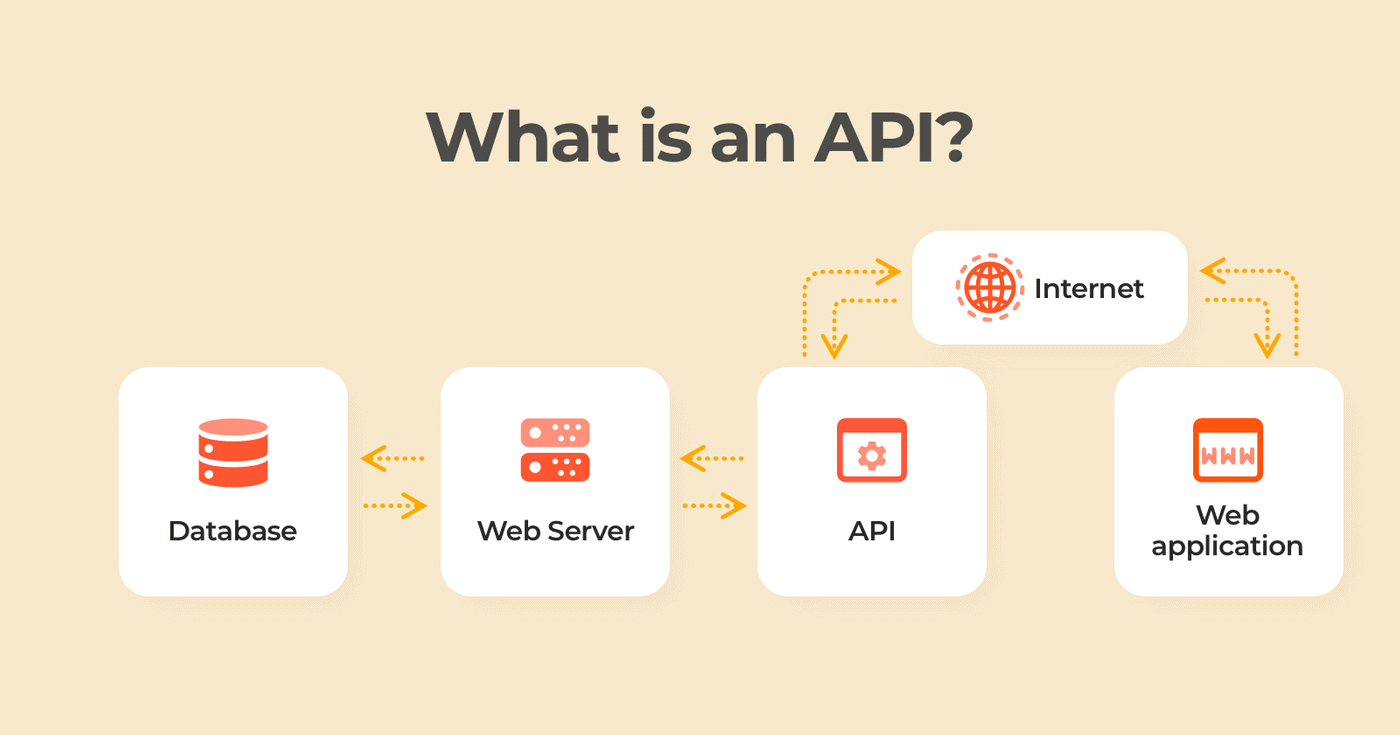
API (acronym for Application Programming Interface) is a particular interface (a collection of commands/controls) developed for rapid interaction between different applications.
The applications may be created in any programming language, run locally or remotely, and reside on individual servers or in the cloud infrastructure. This is irrelevant. The important point is that API allows them to “understand” and communicate with one other: exchange data, send/receive execution directives, and so on.
A single communication format (protocol) should be agreed in advance to make the API clear for both parties. As a result, APIs are extensively described so that developers of other programs that are external to your interface may take your data format and demands into consideration when developing their product.
Type of API
Now that you know what an API is and what it does, it’s time to look at the many types of APIs accessible. While APIs perform comparable operations at their core, they might differ slightly in their implementation.
REST API
REST stands for Representational State Transfer. It is also called RESTful APIs. REST APIs have become more popular recently as a component of Web Services.
When you open Instagram and search for the latest meme of today, a developer’s API is being used. This special type or programmable interface enables an application to interact with another service in order accomplish tasks like getting data from it (in this case), creating new posts on your behalf – all without writing any lines yourself!
SOAP APIs
Simplified Object Access Protocol is what SOAP stands for. As an architectural style, REST stands in contrast to the more standard-based SOAP. As XML-based systems and programming are required for SOAP, the protocol’s data is typically larger and more expensive. To top it all off, SOAP APIs provide a more robust safeguard. One such scenario involves an application interacting with a bank.
RPC APIs
It’s common to refer to this method of communication as “RPC” for short. The first APIs, known as remote procedure call APIs (RPC APIs), allowed developers to launch a predefined sequence of instructions on a remote server. The use of HTTP might transform it into a Web application programming interface.
Conclusion
Companies continue to see the potential of extending and integrating application data flows through APIs, which makes it easier to integrate business processes across applications when used with other types of B2B technology. This is because APIs improve speed, agility, consistency, and accuracy in many industries.
APIs are now an essential part of running a data-driven business. They let business users and IT use software and applications to improve productivity and the bottom line. Using APIs can pay off for an enterprise in many ways, from social collaboration tools to more creative ways to reach out to customers.